What is Melanoma?
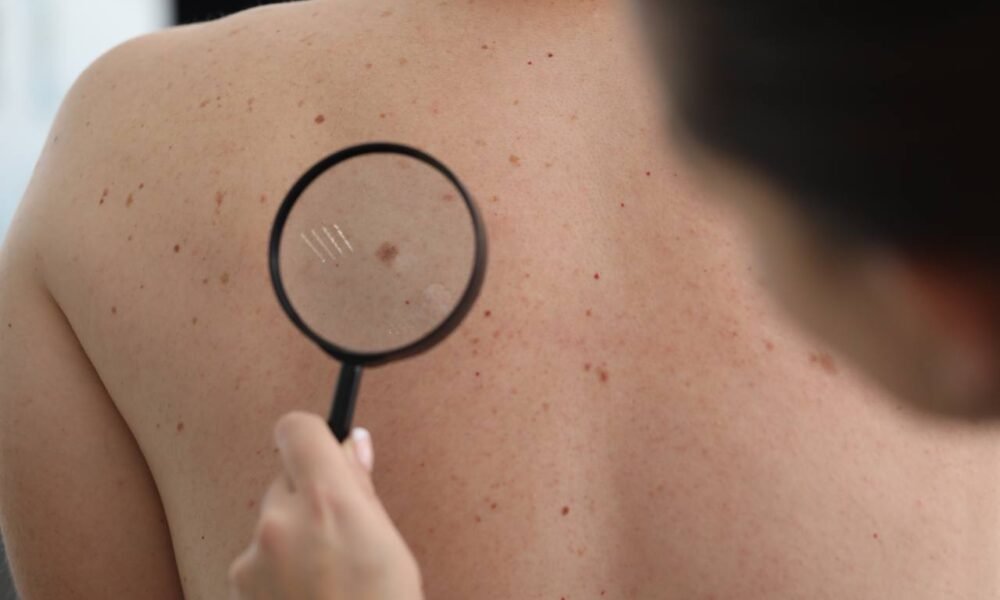
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops in the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color. It can appear on any part of the body but is most commonly found in areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, hands, and legs. Melanoma can also develop in areas not typically exposed to the sun, including the palms, soles of the feet, and under the nails.
What are the Symptoms of Melanoma?
- Asymmetrical moles or growths
- Uneven or irregular borders of a mole
- Changes in the size, color, or shape of a mole
- Itching or bleeding in the mole area
Preventing Melanoma
While certain factors that increase melanoma risk, such as genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps people can take to lower their risk of developing this disease:
- Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours
- Wear protective clothing, including hats and sunglasses, when outdoors
- Use sunscreen with a high SPF
- Avoid tanning beds, which emit harmful ultraviolet rays
Melanoma Treatment Options
Treatment for melanoma depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, its location, and the person’s overall health:
- Surgical removal: Removing the melanoma along with some surrounding healthy tissue
- Radiation therapy: Targeting and destroying cancer cells
- Chemotherapy or immunotherapy: Destroying cancer cells or boosting the body's immune response to fight cancer
Melanoma is a serious and potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer, but early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis. By understanding the symptoms, taking preventive measures, and seeking medical help if needed, individuals can reduce their risk of developing melanoma and increase the likelihood of successful treatment outcomes. Stay informed, vigilant, and prioritize your skin health to protect against melanoma.